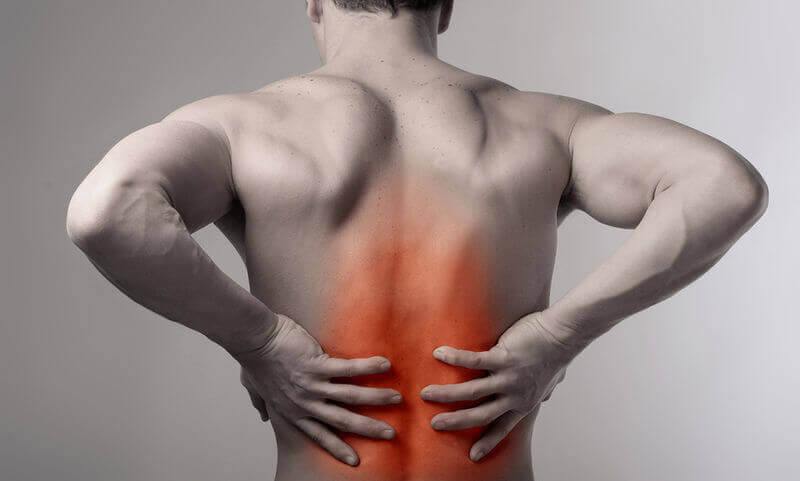
Back pain is a common issue that many people experience at some point in their lives. While most cases of back pain are not serious, it can be difficult to know when it’s time to seek medical attention.
Back pain is a common complaint among people of all ages and lifestyles, and it can have a significant impact on daily activities and quality of life. Whether it’s a dull ache or sharp pain, the discomfort can make it challenging to perform everyday tasks, participate in recreational activities, and even get a good night’s sleep. The good news is that there are many treatment options available to alleviate back pain and improve mobility. In this article, we will explore the symptoms and causes of back pain, and provide effective treatments to help you get back to feeling your best.
Back pain can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Muscle strain: Overuse or improper use of back muscles can cause strain or sprain, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Herniated disk: A herniated disk occurs when the soft tissue between the vertebrae in your spine bulges out and puts pressure on nerves, causing pain.
- Osteoarthritis: This type of arthritis causes the cartilage between your joints to break down, which can lead to pain and stiffness.
- Spinal stenosis: Spinal stenosis is a condition where the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on nerves and causing pain.
- Scoliosis: Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves to one side, which can cause back pain and discomfort.
When it comes to treating back pain, there are several solutions available that can be tailored to your specific needs. These may include physical therapy, exercise, medication, and, in some cases, surgery.It’s essential to work with a medical professional to identify the underlying cause of your back pain and develop a treatment plan that works best for you.There are a number of ways to address back pain, depending on the underlying cause. Here are a few effective solutions:
- Exercise: Gentle exercises can help strengthen your back muscles, alleviate pain, and prevent future issues.
- Heat or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Pain relief medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate mild to moderate pain.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can help you develop an exercise program tailored to your specific needs and goals.
- Surgery: In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to address the underlying issue causing your back pain.
The severity of back pain can vary greatly, but there are some signs that suggest it may be a more serious condition. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s recommended that you seek medical attention:
- Intense pain that doesn’t improve with rest or over-the-counter pain medications.
- Numbness or tingling in your legs, arms, or other areas of your body.
- Weakness in your legs or difficulty walking.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Unexplained weight loss.
If you experience any of these symptoms along with your back pain, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
The most common cause of back pain is muscle strain or sprain. This type of back pain is often caused by overuse or improper use of back muscles, such as lifting heavy objects incorrectly or sitting for long periods of time. The good news is that muscle strain can often be addressed with rest, gentle exercise, and over-the-counter pain relief medications. If your back pain persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, it’s important to consult a medical professional to rule out more serious underlying conditions.